This website is intended for UK healthcare professionals.
The Adverse Event Reporting and a link to the Prescribing Information can be found at the bottom of the page.
Elvanse could open up a world of new opportunities:
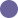
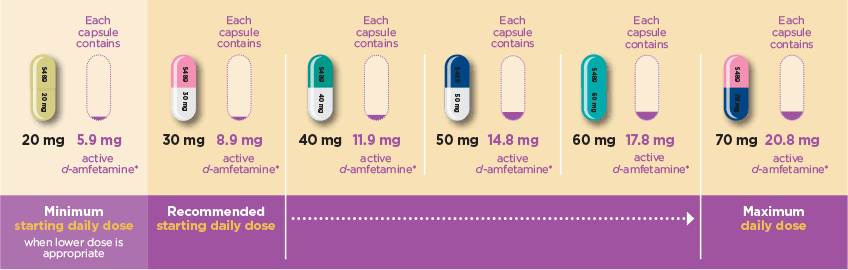
Elvanse® (lisdexamfetamine dimesylate) is indicated as part of a comprehensive treatment programme for ADHD in children aged 6 years and over when response to previous methylphenidate treatment is considered clinically inadequate.2
Treatment must be under the supervision of a specialist in childhood and/or adolescent behavioural disorders.2